Can Baby Male and Female Alligator Snapping Turtle Stay in the Same Tank
Prehistoric and majestic, the Alligator Snapping Turtle is a massive predator in the wild that is native to the Due north American continent.
It is the biggest freshwater turtle in the southeastern United states and is besides one of the heaviest turtles in the world having been recently outweighed by the Hoen Kiem Turtle, a giant soft shell turtle.
The Alligator snapping turtle gets its name considering of its immensely powerful jaws, leap-like neck and a singled-out ridged vanquish that is quite similar to an alligator's rough skin.
Alligator Snapping Turtle
?
Image credits: reptiles4all/Shutterstock
Physical Description
The Alligator snapping turtle is a unique species, the simply i of its kind that shares a genetic background with the extinct prehistoric Carbonemys cofrinii. The Alligator snapper is a massive turtle that can hands trounce other turtles in one-half considering of the colossal size and enormously potent jaw basic. The species is sometimes described as dinosaur-similar considering of its primitive-looking appearance and spiky shell. Dissimilar all other species of the snapping turtles, the Alligator snapper has eyes located on both of its sides. It is the largest freshwater turtle that typically weighs betwixt 45-175 lb and generally attains an average length of i.1-2.half-dozen ft.

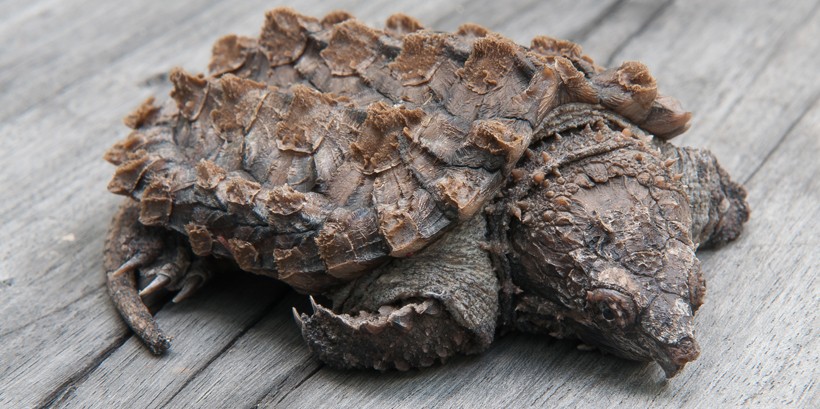
Primitive-looking Alligator Snapping Turtle
?
Epitome credits: reptiles4all/Shutterstock
While being one of the heaviest turtles on earth on boilerplate, there have been findings of even larger specimens similar the sixteen-year-sometime resident giant Alligator snapper in 1999 that weighed 249 lb at the Tennessee Aquarium. Another weighing 236 lb was housed at the Brookfield Zoo in Chicago that reached a maximum carapace length of 2.eight anxiety. At that place is sexual dimorphism within the species where the male adult is larger than the female snapper and also the position of the cloaca varies per gender. The lifespan of a typical Alligator snapping turtle tin can be anywhere betwixt 11 – 45 years although a few examples have been recorded to alive equally long every bit 70 years.
Geographical Distribution
The Alligator snapping turtle is native to the Due north American continent and is located in freshwater habitats and wetland swamps. They are primarily situated in the southeastern United States occupying regions similar northern Florida, eastern Texas, southeastern Iowa, western Illinois and southern Georgia. They can be found also north to southeastern Kansas, northern Gavin's Signal Dam, western Tennessee, southern Indiana, western Kentucky and across the Missouri River at Yankton, South Dakota.
Habitat
Alligator snappers prefer a freshwater habitat and are usually living in deep waters of big rivers, lakes, canals and swamps. While hatchlings are bred near surface water and near smaller streams, adults are generally bars to river systems that bleed in the Gulf of United mexican states. Male person alligator snappers spend virtually of their time underwater whereas females generally venture on country during the breeding season. The species resides in a temperate climatic zone that consists of marshy fields, freshwater river beds and brackish wetlands.
Beefcake
Alligator snapping turtles are known as the 'dinosaurs of the turtle earth' because of their prehistoric appearance. The rugged, spiky carapace or ridged upper crush camouflages brilliantly in the wild, making the Alligator snapper an elegant predator. The species has a big caput, powerful built, hooked pecker like jaws, oversized claws and a scaly, rough skin that sets it apart from other freshwater turtles.

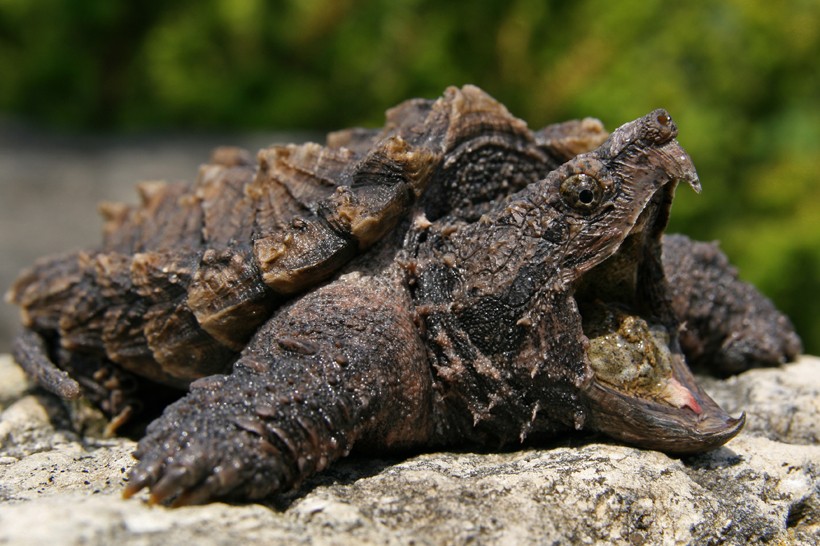
Spiky carapace of the Alligator Snapping Turtle
?
Prototype credits: Sista Vongjintanarug/Shutterstock
The 3 large pronounced ridges, that run across the full dorsum of its dark-brown to blackish vanquish, resemble the rugged skin of an alligator. The Alligator snapper showcases bilateral symmetry and is, similar all reptiles, an ectothermic being. This colossal predator is omnivorous and feeds on both plants as well as the flesh of invertebrates, aquatic crustaceans and fish. Though it is known as the alligator snapping turtle, the bite forcefulness recorded is lesser as compared to other turtles and is almost equivalent to a human being's bite strength relative to the turtle's body size. The species is capable of biting through the handle of a broom and there are rare cases where human being fingers take also been bitten off.
Sexual dimorphism is credible in the species by the singled-out location of the cloaca on the male and female snapper. In female person alligator snappers the cloaca is based on the border of the carapace whereas in males the cloaca extends beyond the edge of the carapace. The tail is equally long equally the shell itself all the same the size differs in both male and female person alligator snappers. Apart from size, the base of the tail in males is thicker as compared to females considering of the reproductive organs that are subconscious. Together with the chin, neck and throat, the peel is coated with long, pointed tubercles. The interior of the turtle's oral cavity is camouflaged and at that place is a vermiform appendage (worm-shaped appendage) located at the tip of the natural language which is used to lure fish, an accommodation known as the Peckhamian mimicry. This appendage is generally grey at first just suffused with blood that is wriggled to concenter prey into the turtle'due south mouth. The trounce of the turtle often has algae growing on it that aid the animal to cover-up itself in the wild.
Feeding Habits
The alligator snapping turtle is an omnivore that consumes both meat and plants although information technology prefers invertebrates and fish more often. Information technology is an opportunistic feeder that relies on both living foods also equally dead organisms which it can scavenge. In full general, the species swallow almost annihilation they can go their hands on. The alligator snapping turtle mostly prefers to grab prey, like for example fish, that is abundant and easy to prey on. Their diet primarily consists of fish and fish carcasses, mollusks, carrion, crustaceans and amphibians. They are also known to casualty on snakes, crayfish, worms, aquatic plants, water birds and other turtles. On certain occasions the species may also prey on aquatic rodents, muskrats, nutrias and modest to mid-sized mammals like squirrels, opossums and armadillos caught more often than not most the water's edge.

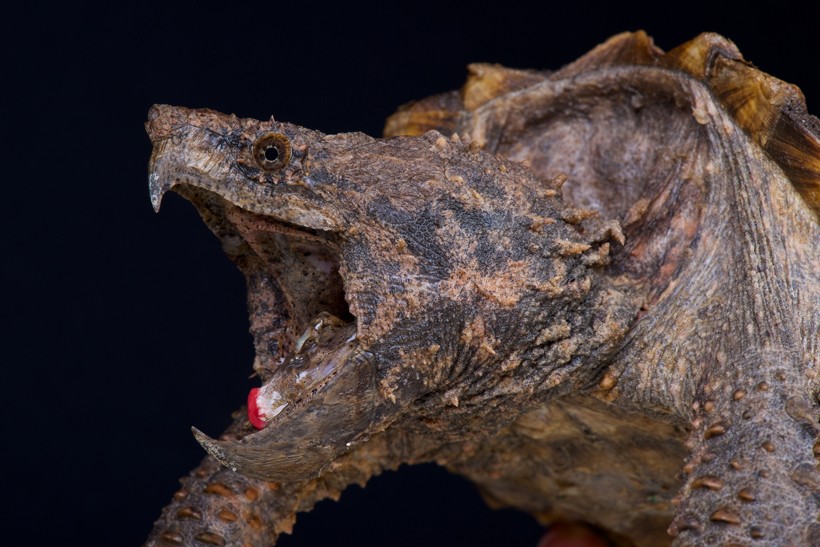
The snapper uses its tongue to lure prey near plenty for a strike.
?
Image credits: Ryan Thou. Bolton/Shutterstock
Alligator snapping turtles are nocturnal hunters, primarily being active at dark when the temperature conditions are suitable. During the day they lie quietly at the bottom of murky water keeping their jaws open and waiting for their prey. The snapper uses its tongue to lure casualty near enough for a strike. The natural language is wriggled to mimic the movements of a worm that generally attracts fish and several invertebrates towards the predator. Immature alligator snappers use this technique to catch small fish like minnows. Adults, however, must forage more actively to satisfy their voracious appetites.
They also employ certain sensory organs to detect prey by tasting chemicals in the water that bespeak the presence of a certain species. Another regular food source for alligator snappers are plants similar basics, seeds, wood, bark, roots, leaves or stems.
Predator
Alligator snapping turtles are large enough to be considered major predators in the wild. All the same, despite their size and rocky built, also this species confront certain threats, especially from humans. Hatchlings are often preyed on past raccoons, predatory fish, large birds and freshwater alligators. Humans find the alligator snapping turtle quite valuable for its meat and appearance. As a consequence, illegal trade and hunting are common problems for this species.
Reproduction
The mating season for Alligator snapping turtles begins in early jump in the southern part of the continent like Florida and late spring in northern ends like Mississippi Valley. The species is polygynandrous which means both male and female snappers mate with more than one partner. The breeding is seasonal and information technology takes place once a twelvemonth. The species reaches sexual maturity within xi – 13 years. During the convenance season, Alligator snappers are quite territorial and upon finding a potential female mate, they mountain the back of the female as a form of showing their approval. They grasp the shell of the female snapper using their sharp, crooked feet to induce insemination. The fertilization is oviparous where the female lays eggs in a nest, which is a dug hole approximately 50 thou from a water source. The nest is dug in the sand and the clutch size depends upon various factors.
A clutch may incorporate as many as viii – 52 eggs and incubation generally persists for 100 – 140 days. Hatchlings tend to be born in the fall and are independent at birth which is besides why they frequently become like shooting fish in a barrel prey for brutal predators. The sexual orientation of the newborn depends on the incubation temperature. The newborn alligator snappers are very like to adults in terms of their advent. Where females more often than not are born if the incubation temperature is around 29 – 30 caste Celsius, males are born when a lower incubation temperature status of 25 – 27 degree Celsius has existed. Baby alligator snapper turtles feed on snails, guppies, tadpoles, crayfish and other pocket-size invertebrates in the h2o.
Behavior
Alligator snapping turtles are massive predators with a archaic appearance, hence they are besides known as the 'dinosaurs of the turtle world'.
Initially, it was considered that the Alligator snapping turtle had 2 more subspecies. However, today all three take been differentiated into three divide species. They are the largest freshwater turtles found in Due north American waters that spend most of their time in the h2o and more often than not just come up out to relish in the sun. They are alone creatures that show little to less parental care. While adult alligator snappers reside in rivers, swamps and canals, the hatchlings stay nearly small streams. The most distinguishing feature of the species is the presence of three dorsal ridges of big scales on the shell that give it a prehistoric appearance. With radiating xanthous patterns around the optics and algal growth on the carapace, the species gets naturally camouflaged in the wild.
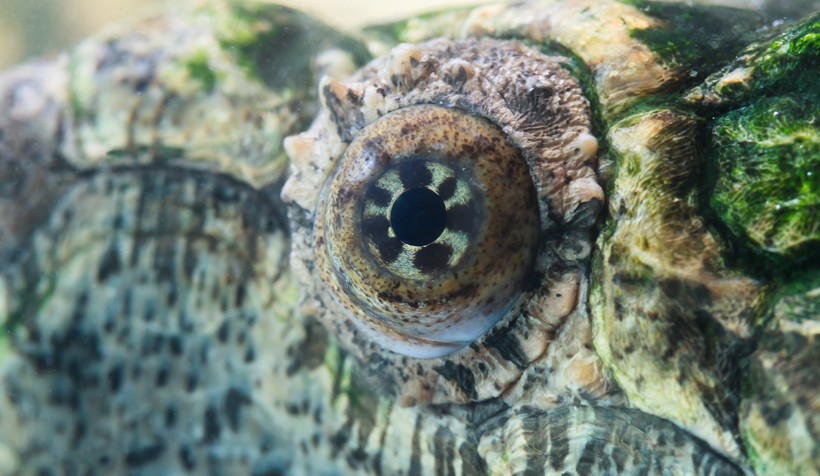

Radiated centre pattern of the Alligator Snapping Turtle
?
Image credits: Webitect/Shutterstock
The alligator snapping turtle is an ambush predator that waits to catch its prey in water and generally luring the prey using its natural language. A fascinating accommodation of the Alligator snapper is its natural language that is shaped like a worm which information technology wriggles to attract prey. The Macrochelys temminckii is a bottom feeder that is mostly active at nighttime and is known to feed often on decaying remains. Alligator snappers generally eat all year circular. Still, they reject to consume when the temperature is high and therefore prefers a warm winter flavour to search for food in water and along the shoreline. The species shows seasonal migration where a few populations are known to brand extended movements at detail times of the year for finding hibernation sites and breeding grounds. Fifty-fifty though they drift on a local base of operations, older individuals generally move upstream as years pass by. The species is quite aggressive when defending itself and shows very piffling social interaction.
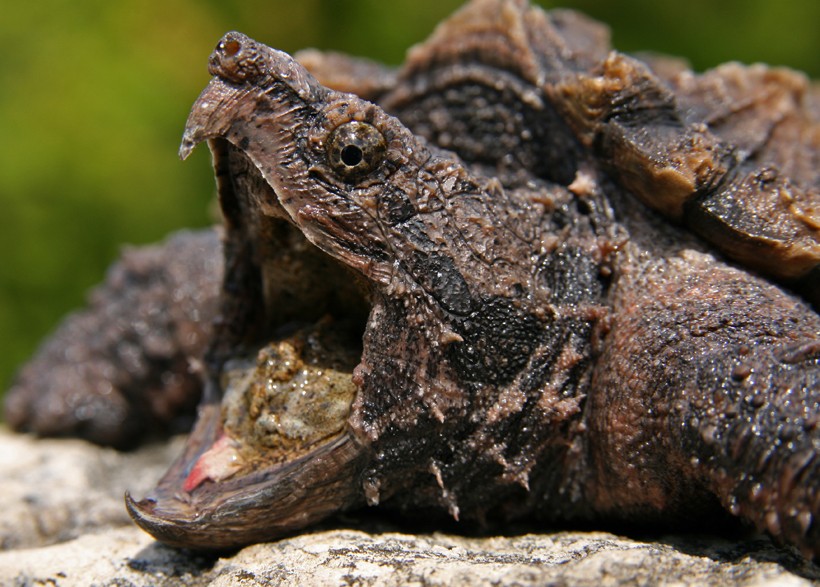

The Snapping turtle is quite ambitious when defending itself
?
Image credits: Ryan Yard. Bolton/Shutterstock
Generally, if an Alligator snapping turtle is forced to go out its resting spot information technology becomes agitated and very aggressive. If attacked or picked up the snapper will shoot its head forward with incredible speed and will use its enormous jaw to bite. It extends its cervix forward and closes its jaws with a loud crisis grabbing onto its assailant with a bite strength that can easily deliver a painful wound. Sometimes the species likewise likes to bury themselves in the mud with just its nostrils and eyes exposed, which is another adaptation to catch casualty. Principle predators of the alligator snapper are humans which is why the species has go elusive and shows secretive traits. In terms of advice, the alligator snapper uses chemosensory cues to locate its prey. They employ throat (gular) pumping to draw in water for sampling changes in the surround. They as well apply certain leg movements to communicate with their mates in the breeding season.
Threats
Alligator snapping turtles accept no natural predators in their native environment. Nonetheless, due to homo interference the population has suffered a massive reject. The species is hunted by poachers for its meat and the shell. Major exploitation of the species is also being caused past trappers who take hold of the species for illegal pet trade and for harvesting the carapace. Due to overharvesting of its meat, habitat destruction and collection for exotic pet trade, there is dire need for federal protection. The species has therefore been listed equally 'Threatened' in several regions of the United states of america where illegal hunting of alligator snappers accept been banned.
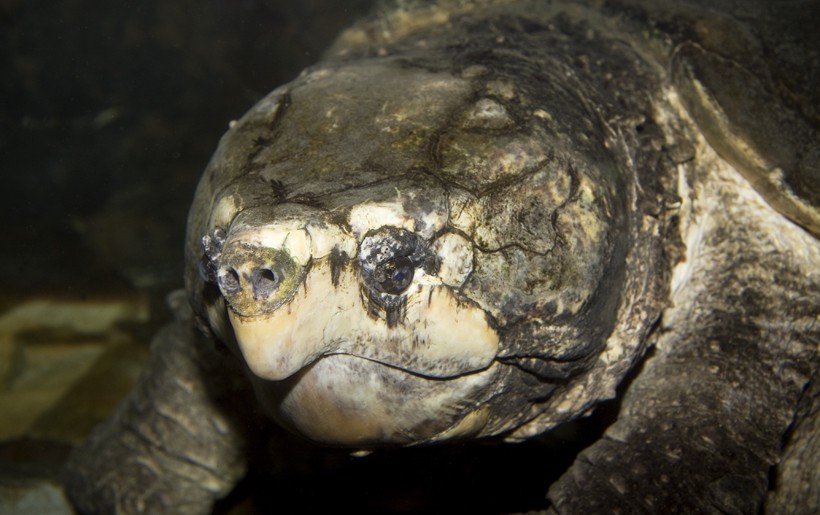

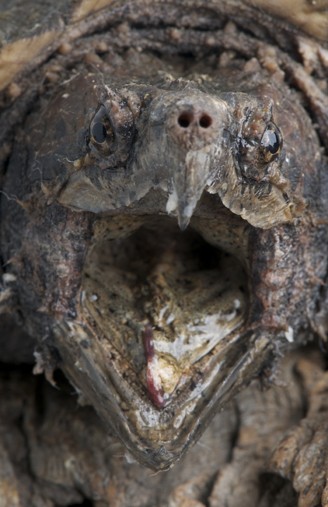
Closeup head Alligator Snapping Turtle
?
Image credits: Jeff Grabert/Shutterstock
Information technology was in July 2012 that many scientists like E.O. Wilson, Kenneth Krysko and Thomas Lovejoy petitioned for federal protection of the species. According to a recent study, the population of alligator snappers in Iowa, Illinois, Tennessee, Missouri and Kentucky has faced massive decline over the years. There are still many illegal tradesmen who commercially exploit the species causing instability of the alligator snappers population. An alarming fact is that much of their habitat has been drained of its resources and converted into croplands, thereby limiting their distribution.
Conservation
Co-ordinate to the IUCN Red Listing, the species is listed as 'Threatened' and has been given protection after information technology was placed in the CITES Appendix II on June xiv, 2006. The Florida Fish & Wildlife Conservation Commission currently lists the species of 'Special Concern' and prohibits its capture from the wild. Apart from illegal hunting, the species also suffers from local threats like incidental trawling, nest predation, water pollution and riverine habitat amending. Habitat loss has affected the convenance bicycle of the species causing a decrease in the population and degeneration of the gene pool. However, the Imperiled Species Management Plan led by the F.A.C focuses on decision-making the population in Florida by introducing strategic methods for improving water quality, conserving individual lands that border their habitat and several other activities. Recently the state of Illinois has been reintroduced the species to strategic watersheds that take been synthetic to preserve its native gene pool.
Funfacts
- Alligator snapping turtles can stay submerged underwater for a period of 40 – 50 minutes earlier they emerge for air.
- They are the only species of turtles that are known to preserve a predatory lure adaptation in their mouths.
- The oldest alligator snapping turtle that was bred under captive care is known to take lived for 70 years.
- Dissimilar nearly snapping turtles, the alligator snapping turtle has optics that are located on the sides of its head.
- As soon as the prey enters an alligator snapper's mouth, it will either swallow it whole or slice information technology in two halves using its stiff jaws.
- Alligator snappers are the largest freshwater turtles in the U.s..
- Alligator snappers are considered 'in need of conservation' in the city of Kansas.
- The Alligator snapper has a triangular head, rocky built, dorsal ridges and little bumps that look like eyelashes, giving information technology a prehistoric look.
- Alligator snappers should never be picked by their tails since it causes massive damage to their spinal cord.
Source: https://www.aboutanimals.com/reptile/alligator-snapping-turtle/
0 Response to "Can Baby Male and Female Alligator Snapping Turtle Stay in the Same Tank"
Post a Comment